Nucleation
Nucleation is widely studied in many scientific and technological processes; however this blog is inspired by a relatively new field of application, phase-diagram-on-a-chip. Generally speaking, phase diagrams are graphs used in the field of physical chemistry to show various phases of a substance with changing conditions of pressure, temperature, etc. When a phase diagram is directly generated on a micro-chip (as opposed to the traditional way of drawing it on a page from experimental data) it is called a phase-diagram-on-a-chip.
Modeling Open Surface Microfluidics
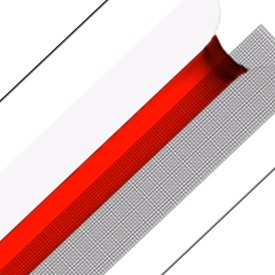
In a recent paper from researchers from the University at Buffalo and University of Grenoble, it was shown how microgrooves can potentially enhance the capillary effect. Based on the results of this paper, I will discuss a case study of the spontaneous capillary flow of fluids inside a narrow V- groove microchannel surmounted by parallel plates using FLOW-3D. Large fluid velocities can be obtained, even with viscous fluids such as whole blood for the design of POC systems to monitor blood flow, if certain conditions for the onset of capillary flow are satisfied.
Micromixing Using Curved Microchannels
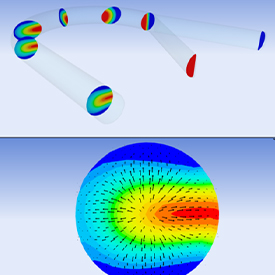
Mixing fluids can be very important in the design of miniaturized chemical and biochemical analysis systems. However, the mixing of fluids at the micro-scale is challenging because of an inherent lack of any mechanism to induce the mixing. Turbulence is a good natural way to cause mixing, but microfluidic processes are laminar in nature. In this blog, I will talk about the challenges that arise because of the laminar flow regime and ways to overcome those challenges when designing micromixing devices.
New Die Spray Cooling Model
In this last blog on FLOW-3D CAST v4.2’s developments, I discuss the new Die Spray Cooling Model for thermal die cycling simulations. The new model provides accurate temperature distribution on the die surfaces with reliable and realistic input parameters, which helps engineers to better design and optimize the cooling process to eliminate hot spots. A sample thermal die cycling simulation demonstrates the capability of the new model, and the importance of explicitly simulating the die spraying process.
HPDC Process-oriented Workspaces
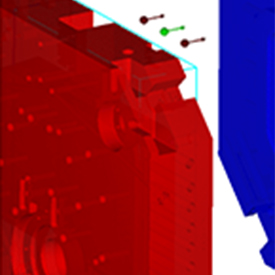
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) simulations are typically very complex as they include almost all of the possible physical processes including heat transfer, melting/solidification, air entrainment, surface defect tracking, and cavitation. As a result, setting up casting simulations can be quite time intensive and error prone. HPDC Process-oriented Workspaces have been added to FLOW-3D CAST v4.2 to help users create simulations quickly and free of errors.
WYSIWYN – What You See Is What You Need
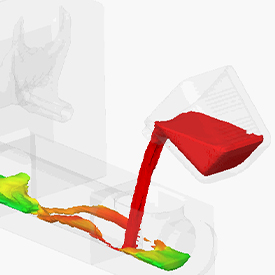
Later this month, our metal casting users will be WYN-ing with the release of FLOW-3D CAST v4.2. This new release features a streamlined user interface designed with a focus on WYSIWYN – What You See Is What You Need. The FLOW-3D CAST v4.2 interface will make simulation setup more efficient and error free by providing a consistent layout and a flat design that shows users the most important simulation information on the top level.
Non-Inertial Reference Frame Motion
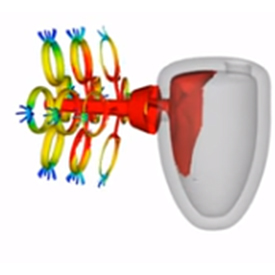
Adapting non-inertial reference frame model results to enable visualization from a stationary frame of reference is a nifty new feature coming in the upcoming releases of FlowSight™ for FLOW-3D CAST v4.2 and FLOW-3D v11.2. This brief note describes this feature and gives a couple examples.
Microfluidic Circuit – Pneumatic Latching Valve
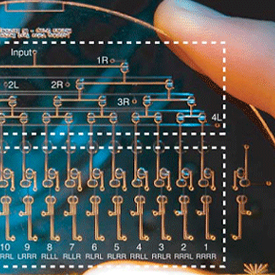
In this final post in the series of Flow Science’s 35th anniversary simulation contest, I will talk about a case study simulating a part of a microfluidic circuit – pneumatic latching valve. These devices are a relatively new industry application that Flow Science is exploring, in the context of a broader exploration of the use of CFD in microfluidics applications, and results have been very encouraging.
Simulating Pelton Turbines
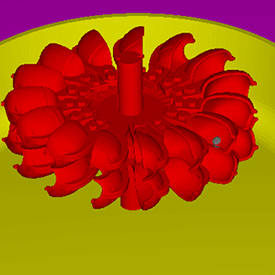
Pelton turbines are used for electricity generation in hydraulic power plants. They are suitable for operation when water energy is available at high head and low flow rate. In a Pelton turbine, the energy extracted from the kinetic energy of the water is used for the rotation of the impeller.
Floating Structures
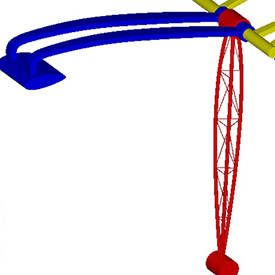
Floating structures on an ocean surface, restrained by mooring ropes, are a common sight in the oil and gas industry. The problem of understanding the dynamic response of a floating structure becomes challenging due to the complex dynamics of the system. In this article, I will talk about the dynamic response of a floating structure made of 3 elements hinged together, followed by a presentation of FLOW-3D simulation results.
Cavitation Model Improvements
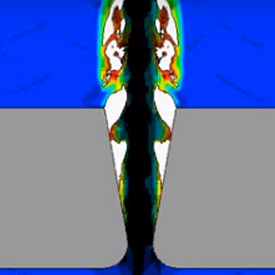
Cavitation is the evolution of vapor and/or gas bubbles within liquid in the regions of low pressure in the flow, or due to heating that raises the vapor saturation pressure. The sudden appearance and subsequent collapse of bubbles may cause large oscillations of pressure within incompressible fluid that in turn result in severe mechanical damage to the surrounding structures.
New Boundary Conditions

For numerical modeling of river flows, typically water elevation is required at the upstream boundary. Yet water elevation in natural environmental systems is often unknown and has to be estimated. Improper elevation estimation, however, can generate nonphysical results.
Raster Data Interface
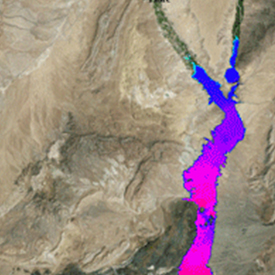
FLOW-3D allows users to import solids in STL (StereoLithography) format to represent complex geometries, regardless of the application – micro fluids, metal casting, water and environmental, aerospace, etc. In the upcoming release of FLOW-3D, we have adopted an industry norm for terrain import: the file format known as the ESRI ASCII raster format.
P-Q Squared Analysis
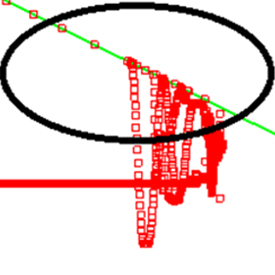
P-Q squared analysis is a standard procedure used to optimally match the target gate velocity to the capabilities of the HPDC (High Performance Die Casting) machine’s plunger hydraulic system. Desired fill time and an optimum gate design can be attained by performing P-Q squared analysis, which in turn, maximizes the efficiency of the HPDC system.
Solid Propellant Combustion Modeling
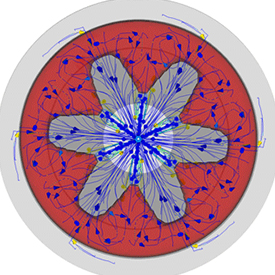
Solid fuel combustion is a traditional method of extracting energy from solid objects. However, an important relatively new application of solid fuel combustion is in rocket propulsion. The development of the Combustible Objects model in FLOW-3D was motivated by solid propellant combustion in rockets.
